- Addition of rational numbers
To add two rational numbers, first express each rational number with a positive denominator.



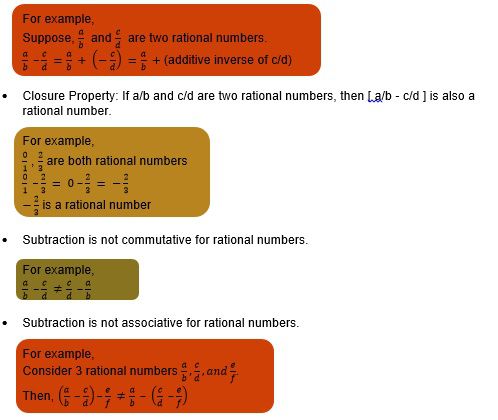
Subtraction of rational numbers
Subtracting one rational number from another rational number is same as adding the additive inverse(negative) of the rational number that is being subtracted to the other rational number
EXAMPLE 1: Sum of two rational number is 1/6. If one of them is -1/2, then find the other rational number.
SOLUTION: The other rational number is = 1/6 – (-1/2) =1/6 + ½ = 2/3 [ANS]
EXAMPLE 2: What number should be added to -1/4 to get -4/5?
SOLUTION: The number is = -4/5 – (-1/4) = -4/5 + ¼ = -11/20 [ANS]
Multiplication of rational number


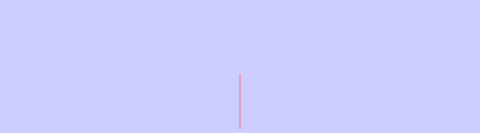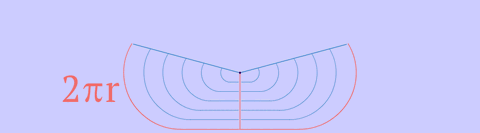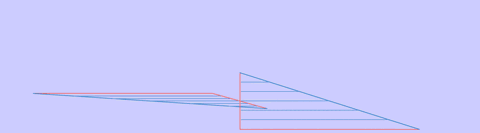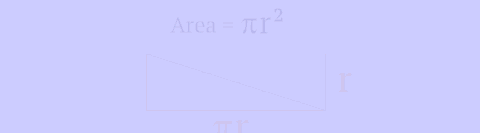
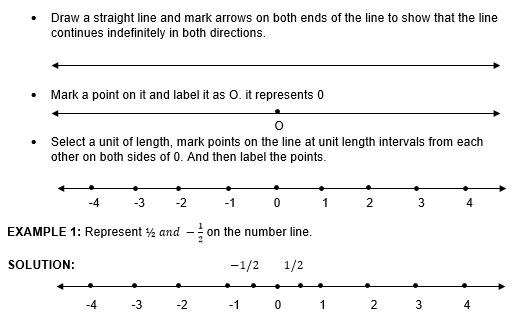
Representation of a rational number on a number line
To represent rational number on a number line proceed as under:

Rational numbers between two rational numbersTo insert n rational numbers between two rational numbers, do the following:
- When given rational numbers have the same denominator multiply the denominator and numerator by (n+1).
- When given rational numbers have different denominators: find the LCM of the denominators; change the given rational number into equivalent rational numbers with LCM as their denominator; If necessary multiply the denominator and numerator of each by (n+1).

Practice these questions

Q4) Vivan donated of his salary to the orphanage, 1/4th of his salary on food, 1/3 of his salary on rent and electricity, and 1/15th of his salary on telephone bills. This month he donated Rs. 6000 in a charity. He is left with Rs. 4000. Find his monthly salary.
Q5) Area of a square is 1 sq. metre more than ½ of the area of a rectangle. If the area of the square is 91 sq. metre. Then find the dimensions of the rectangle. Given breadth is ¾ times of length.

Recap
- All integers and fractions are real numbers
- Addition is closed, commutative, associative.
- Multiplication is closed, commutative, associative and distributive
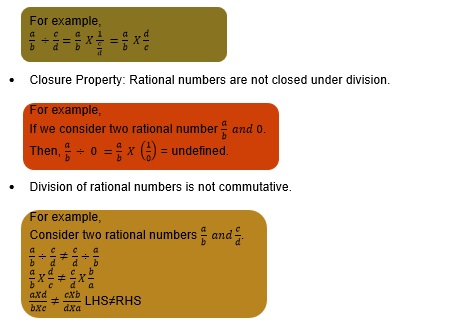
Division is not closed, not commutative, not associative.